Tokenisation begins : All you need to know about the new rules for credit and debit cards
Card tokenisation offers an added layer of security for online transactions. This is how it works.
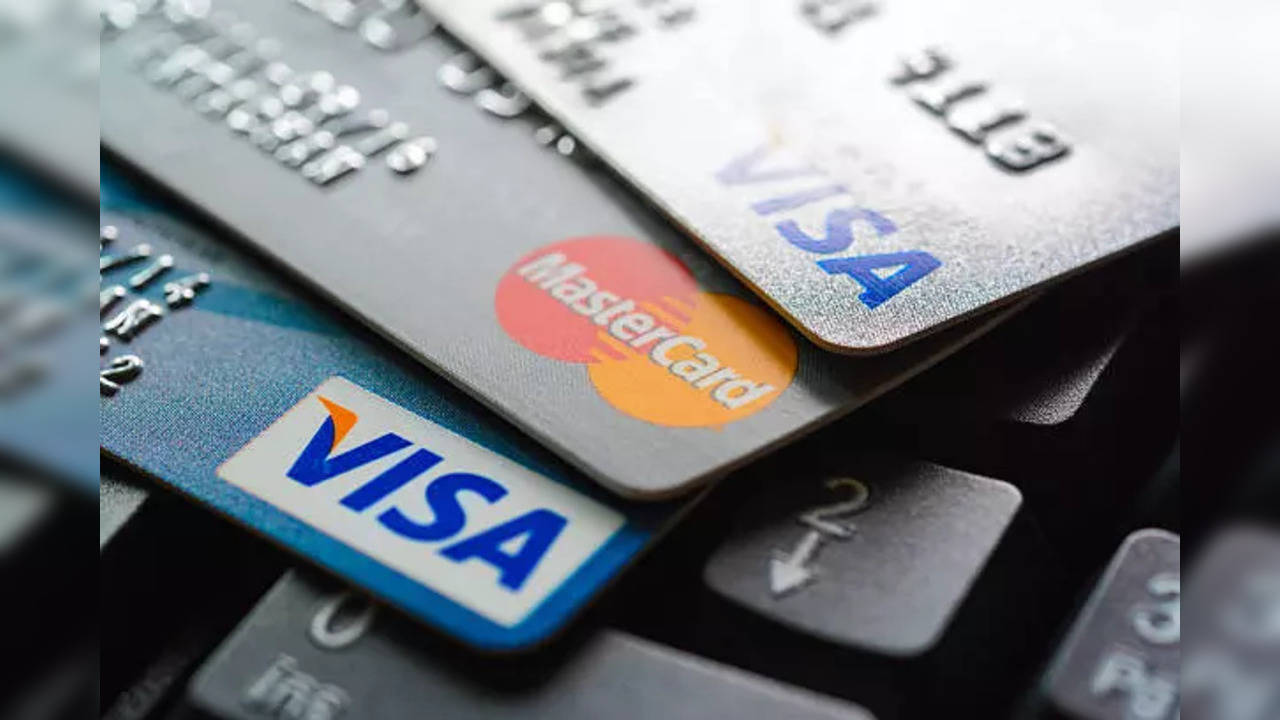

From Saturday, no online retailers or payment gateways will be permitted to save the customers’ credit or debit card details on their platforms.
Photo : iStock
In a measure to improve the security of online transactions, the card tokenisation system has been made effective from today (October 1).
The Reserve Bank of India said in a statement on Friday that it sees no reason to delay the move, first green-lighted in 2019, any longer.
RBI Deputy Governor T Rabi Sankar said ahead of the rollout o Friday, “The feedback we have from all stakeholders is that it (ecosystem) is perfectly ready. I understand there are a few participants who may not be ready, but that would probably be because of their unwillingness to comply. We don’t believe that we should hold back efforts because of such laggards.”
From Saturday, no online retailers or payment gateways will be permitted to save the customers’ credit or debit card details on their platforms.
Merchants would store card details to make recurring payments easier, but the ‘convenience’ came at the cost of ‘security’.
What is tokenisation ?
Actual card details will now be codified. Each payment method will get such an alternate code called ‘token’ which will be unique to it. The code or token will be specific to the combination of card, token requestor (i.e. the entity which accepts request from the customer for tokenisation of a card and passes it on to the card network to issue a corresponding token) and device on which the transaction is made.
A list of card networks authorised by the central bank can be found here https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/PublicationsView.aspx?id=12043
How will transactions work?
You will not be automatically signed up for tokenisation unless you explicitly give consent through Additional Factor of Authentication (AFA). According to the RBI, the customer will also be given choice of selecting the use case and setting-up of limits.
The RBI says, the card holder can get the card tokenised by initiating a request on the app provided by the token requestor.
The token requestor will then forward the request to the card network (like Visa or Mastercard) which, with the consent of the card issuer, will issue a token. The token will be a unique arrangement of letters and numbers that correspond to the combination of the card, the token requestor, and the device.
Consumers can request tokens for multiple cards and they are free to use any card registered with the token requester. The consumer can also request tokenisation from any number of devices.
Is tokenisation fool-proof?
Your card contains a 16 digit number and a security code. If a hacker gets access to these, you can potentially lose money. However, tokenisation is the firewall against this misuse.
It is fool-proof unlike encryption, where anyone with a decryption key can decipher the codes.
Tokenisation involves surrogate numbers/letters that are generated afresh every time that a transaction is made. The token is generated by the card company’s system through a complex set of algorithms using details specific to the transaction like card holder’s details, merchant’s details, device etc as mentioned before.
Before this, the RBI had mandated that an additional layer of security be added by generating OTPs to authorise transactions. This too is an effective mechanism as it is generated afresh each time, however, a token is a more complex alphanumeric code.
Trending:
End of Article
Subscribe to our daily Newsletter!
Related News





Tech Layoffs 2024: Experts Explain Why The Tech Industry Is Most Affected

Who Built NASA's James Webb Space Telescope?

Explained: What Is 60% Kannada Rule That Saw Violent Protests In Bengaluru

Disease X Versus COVID-19: What Are Similarities And Difference Between Two
Are We Prepared to Deal with Disease X?









