Paleontologists find a 541 million-year-old Algae fossil that precedes the genesis of land plants
Furthermore, the fossil is the first and earliest green algae from this age to have been conserved in three dimensions, allowing scientists to analyse its internal structure with unparalleled precision.
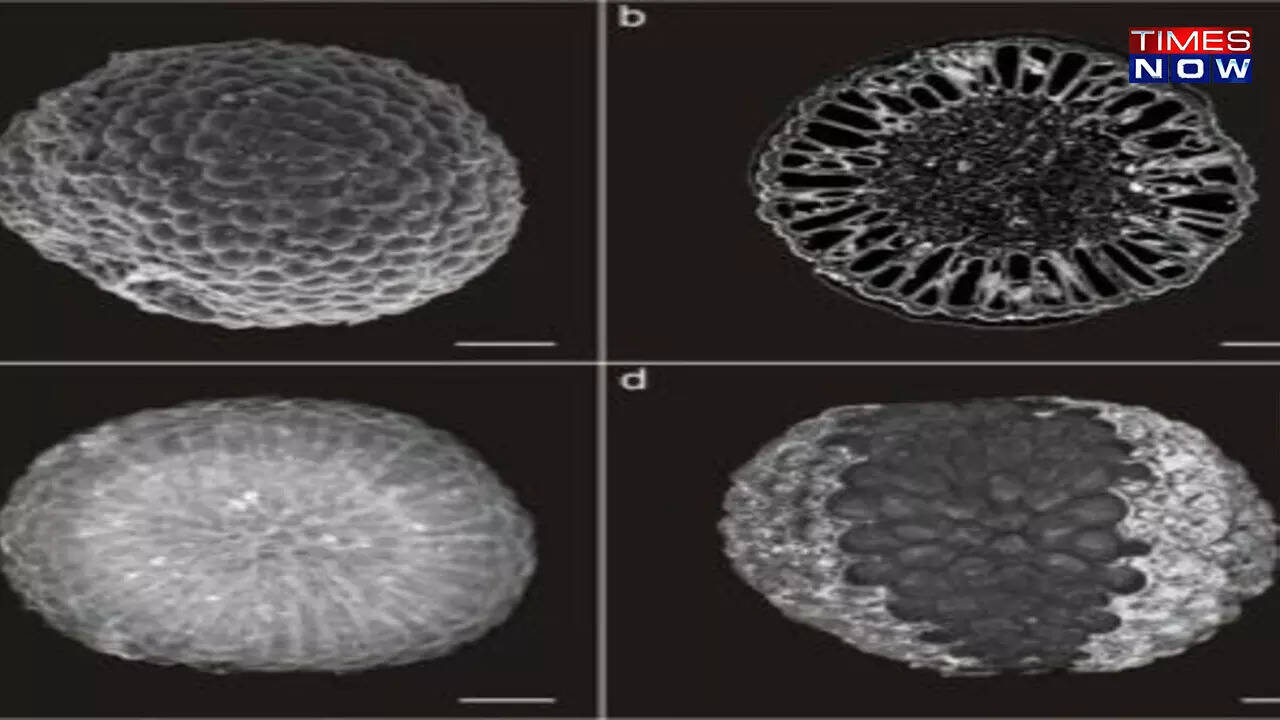
September 26, 2022: Palaeontologists have found an ancient algal fossil in China and named it Protocodium sinense, a novel genus and species. The 541 million-year-old fossil precedes the genesis of land plants, providing scientists with new insights into the plant kingdom's early diversity.
Furthermore, the fossil is the first and earliest green algae from this age to have been conserved in three dimensions, allowing scientists to analyse its internal structure with unparalleled precision.
They discovered that Protocodium looks almost similar to its close relative, Codium - a form of green algae prevalent in many water bodies today - pushing back the time when green algae and land plants had a shared ancestor.
The findings were published in the journal BMC Biology.
Cédric Aria, postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Ecology & Evolutionary Biology at the University of Toronto and based at the Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) in Canada, one of the study's co-authors said, “Protocodium” belongs to a known lineage of green algae and has a surprisingly modern architecture, showing that these algae were already well diversified before the end of the Ediacaran period...Its discovery touches the origin of the entire plant kingdom and puts a familiar name on the organisms that preceded the Cambrian explosion over half a billion years ago, when the world’s first modern ecosystems emerged.”
Green algae can photosynthesise, which means they can transform light and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. They were thus likely crucial underpinnings of Earth's early ecosystems, and the findings suggests that green algae were already entrenched as carbon dioxide recyclers and oxygen makers in the world's shallow waters before the Cambrian explosion.
The Protocodium was discovered as part of the Gaojiashan biota, a large group of unusually well-preserved fossils unearthed in the Dengying Formation in southern Shaanxi Province in northwestern China.
Dr Shu Chai, a postdoctoral researcher at Northwest University in Xi'an, Shaanxi Province, the study's first author said, “We know that seaweed-like fossils are at least one billion-years-old...But until now, flat, grainy two-dimensional preservation has made it challenging to recognise more than general morphological structures.”
The entire fossil and its delicate cellular details were retained in three dimensions through a process known as phosphatisation, in which the original organic material was supplanted by phosphate, enabling researchers to virtually snip through the fossil to unveil its inner constructions using electron and X-ray microscopy.
Protocodium fossils are spherical and tiny (approximately half a millimetre across), with many smaller domes covering the surface. The sophisticated, solitary cell has thin strands called syphons that are encircled by a homogeneous layer of bulb-shaped structures - a feature that is common in certain modern one-celled seaweeds of the genus Codium.
Cédric Aria says, “It’s very telling that such an organism has remained practically unchanged over at least 540 million years."
Aria further adds, “By the Ediacaran, evolution had driven it towards a stable adaptive zone — it’s been comfortable there since, and more than that, quite successful. So much so, in fact, that nowadays Codium takes advantage of global trade to easily outcompete other algal species.”
This article is written by Diya Mukherjee
Trending:
End of Article
Subscribe to our daily Newsletter!
Related News





ChatGPT Down? Users Say OpenAI Chatbot Not Working

TikTok To Be Banned In US, Here Is How China May React

WhatsApp Will Exit India If Forced To Break Encryption, Meta-owned App Warns

Reddit Down: Server Errors Confirmed by Company, User Reports

NASA Hubble Telescope Turns 34: Shares Image Of Mesmerising Little Dumbbell Nebula








